This lesson starts at commit c2c6ad9e07ff149a1de3863f1d10db636e966997.
8. Memory
We'll start with a simple implementation of the memory subsystem, which we need for the load and store instructions. There is quite a lot which we'll need to do for this module, so we'll start on familiar ground and take small steps.
We'll start by implement the store instructions, and specifically, the SW (store word) instruction. The familiar ground we're starting from is the decoder; we'll just do what we have done dozens of times before: Add some decoding logic.
The RISC-V docs say this about the store instructions:
Load and store instructions transfer a value between the registers and memory. [...] The effective address is obtained by adding register rs1 to the sign-extended 12-bit offset. [...] Stores copy the value in register rs2 to memory.
We'll use the first operand to store the address and the second operand to store the value. For now, I'll assume that stores are aligned to a multiple of 4 bytes. The RISC-V specification allows raising exceptions for misaligned memory access (but for now, we will stick to implementing aligned stores, and leave exceptions for later).
|
@@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 38 |
variable j_imm: std_logic_vector(20 downto 0);
|
| 39 |
variable j_imm_s: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 40 |
variable s_imm: std_logic_vector(11 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 41 |
variable u_imm: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
variable v_decode_output: decode_output_t;
|
|
@@ -67,6 +68,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 67 |
b_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(b_imm), 32));
|
| 68 |
i_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(i_imm), 32));
|
| 69 |
j_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(j_imm), 32));
|
|
|
|
| 70 |
|
| 71 |
v_decode_output := DEFAULT_DECODE_OUTPUT;
|
| 72 |
|
|
@@ -141,12 +143,17 @@ begin
|
|
| 141 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 142 |
end if;
|
| 143 |
elsif opcode = "0100011" then
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 144 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 145 |
-- TODO: SB
|
| 146 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 147 |
-- TODO: SH
|
| 148 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 149 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 150 |
else
|
| 151 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 152 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
| 38 |
variable j_imm: std_logic_vector(20 downto 0);
|
| 39 |
variable j_imm_s: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 40 |
variable s_imm: std_logic_vector(11 downto 0);
|
| 41 |
+
variable s_imm_s: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 42 |
variable u_imm: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
variable v_decode_output: decode_output_t;
|
|
|
|
| 68 |
b_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(b_imm), 32));
|
| 69 |
i_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(i_imm), 32));
|
| 70 |
j_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(j_imm), 32));
|
| 71 |
+
s_imm_s := std_logic_vector(resize(signed(s_imm), 32));
|
| 72 |
|
| 73 |
v_decode_output := DEFAULT_DECODE_OUTPUT;
|
| 74 |
|
|
|
|
| 143 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 144 |
end if;
|
| 145 |
elsif opcode = "0100011" then
|
| 146 |
+
-- store instructions
|
| 147 |
+
v_decode_output.operand1 := std_logic_vector(unsigned(reg(to_integer(unsigned(rs1)))) + unsigned(s_imm_s));
|
| 148 |
+
v_decode_output.operand2 := reg(to_integer(unsigned(rs2)));
|
| 149 |
+
|
| 150 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 151 |
-- TODO: SB
|
| 152 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 153 |
-- TODO: SH
|
| 154 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 155 |
+
-- SW
|
| 156 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SW;
|
| 157 |
else
|
| 158 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 159 |
end if;
|
|
@@ -3,7 +3,27 @@ use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
package core_types is
|
| 6 |
-
type operation_t is (
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
type fetch_output_t is record
|
| 9 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
package core_types is
|
| 6 |
+
type operation_t is (
|
| 7 |
+
OP_ADD,
|
| 8 |
+
OP_SLT,
|
| 9 |
+
OP_SLTU,
|
| 10 |
+
OP_XOR,
|
| 11 |
+
OP_OR,
|
| 12 |
+
OP_AND,
|
| 13 |
+
OP_SLL,
|
| 14 |
+
OP_SRL,
|
| 15 |
+
OP_SRA,
|
| 16 |
+
OP_SUB,
|
| 17 |
+
OP_JAL,
|
| 18 |
+
OP_BEQ,
|
| 19 |
+
OP_BNE,
|
| 20 |
+
OP_BLT,
|
| 21 |
+
OP_BGE,
|
| 22 |
+
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
+
OP_BGEU,
|
| 24 |
+
OP_SW,
|
| 25 |
+
OP_LED
|
| 26 |
+
);
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
type fetch_output_t is record
|
| 29 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
Now we want to start implementing the OP_SW operation in the execute stage.
|
@@ -133,6 +133,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 133 |
v_jump := '1';
|
| 134 |
v_jump_address := input.operand3;
|
| 135 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 136 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 137 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 138 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 133 |
v_jump := '1';
|
| 134 |
v_jump_address := input.operand3;
|
| 135 |
end if;
|
| 136 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 137 |
+
-- TODO: implement
|
| 138 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 139 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 140 |
else
|
Hm, we're a bit stuck here. We want to talk to some kind of memory interface or wrapper, which I'll pompously call "memory subsystem". We'll need to output at least:
- An indicator value to indicate we want to write
- The address to write to
- The value to write
The memory subsystem will be placed outside the core, since there are other components that want to "talk" to the memory. So, I'll make a record for these signals, but place it outside of the core folder.
|
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
library ieee;
|
| 2 |
+
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
use work.types.all;
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
package constants is
|
| 8 |
+
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
+
active => '0',
|
| 10 |
+
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 11 |
+
value => (others => '0')
|
| 12 |
+
);
|
| 13 |
+
end package constants;
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
library ieee;
|
| 2 |
+
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
package types is
|
| 6 |
+
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 7 |
+
active: std_logic;
|
| 8 |
+
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 9 |
+
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 10 |
+
end record mem_req_t;
|
| 11 |
+
end package types;
|
Now, we want to make a new module for the memory subsystem.
|
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
library ieee;
|
| 2 |
+
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
+
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
use work.types.all;
|
| 6 |
+
use work.constants.all;
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
entity mem_subsys is
|
| 10 |
+
port (
|
| 11 |
+
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
+
req: in mem_req_t
|
| 13 |
+
);
|
| 14 |
+
end mem_subsys;
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
architecture rtl of mem_subsys is
|
| 18 |
+
begin
|
| 19 |
+
end rtl;
|
Now, we want to instantiate the mem_subsys module in the top_level, and route the signals from the execute stage to the memory subsystem, crossing the interface of the core module. So, here we go.
|
@@ -2,6 +2,8 @@ library ieee;
|
|
| 2 |
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
use work.core_types.all;
|
| 6 |
use work.core_constants.all;
|
| 7 |
|
|
@@ -9,6 +11,7 @@ use work.core_constants.all;
|
|
| 9 |
entity core is
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 13 |
);
|
| 14 |
end core;
|
|
@@ -48,6 +51,7 @@ architecture rtl of core is
|
|
| 48 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 49 |
input: in decode_output_t;
|
| 50 |
output: out execute_output_t;
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
jump: out std_logic := '0';
|
| 52 |
jump_address: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 53 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
|
@@ -67,7 +71,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 67 |
|
| 68 |
decode_write_inst: decode_write port map(clk => clk, decode_input => fetch_output, decode_output => decode_output, write_input => memory_output, pipeline_ready => pipeline_ready);
|
| 69 |
|
| 70 |
-
execute_inst: execute port map(clk => clk, input => decode_output, output => execute_output, jump => jump, jump_address => jump_address, led => led);
|
| 71 |
|
| 72 |
memory_inst: memory port map(clk => clk, input => execute_output, output => memory_output);
|
| 73 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
+
use work.types.all;
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
use work.core_types.all;
|
| 8 |
use work.core_constants.all;
|
| 9 |
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
entity core is
|
| 12 |
port (
|
| 13 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 14 |
+
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
| 15 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 16 |
);
|
| 17 |
end core;
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 52 |
input: in decode_output_t;
|
| 53 |
output: out execute_output_t;
|
| 54 |
+
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
| 55 |
jump: out std_logic := '0';
|
| 56 |
jump_address: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 57 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
|
|
|
| 71 |
|
| 72 |
decode_write_inst: decode_write port map(clk => clk, decode_input => fetch_output, decode_output => decode_output, write_input => memory_output, pipeline_ready => pipeline_ready);
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
+
execute_inst: execute port map(clk => clk, input => decode_output, output => execute_output, mem_req => mem_req, jump => jump, jump_address => jump_address, led => led);
|
| 75 |
|
| 76 |
memory_inst: memory port map(clk => clk, input => execute_output, output => memory_output);
|
| 77 |
|
|
@@ -2,6 +2,9 @@ library ieee;
|
|
| 2 |
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
use work.core_types.all;
|
| 6 |
use work.core_constants.all;
|
| 7 |
|
|
@@ -11,6 +14,7 @@ entity execute is
|
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
input: in decode_output_t;
|
| 13 |
output: out execute_output_t := DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT;
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
jump: out std_logic := '0';
|
| 15 |
jump_address: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := (others => '0');
|
| 16 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0')
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
+
use work.types.all;
|
| 6 |
+
use work.constants.all;
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
use work.core_types.all;
|
| 9 |
use work.core_constants.all;
|
| 10 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 15 |
input: in decode_output_t;
|
| 16 |
output: out execute_output_t := DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT;
|
| 17 |
+
mem_req: out mem_req_t := DEFAULT_MEM_REQ;
|
| 18 |
jump: out std_logic := '0';
|
| 19 |
jump_address: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := (others => '0');
|
| 20 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0')
|
|
@@ -2,6 +2,8 @@ library ieee;
|
|
| 2 |
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
entity top_level is
|
| 7 |
port (
|
|
@@ -12,17 +14,27 @@ end top_level;
|
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
architecture rtl of top_level is
|
| 15 |
-
signal
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
component core is
|
| 18 |
port (
|
| 19 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 21 |
);
|
| 22 |
end component;
|
| 23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
begin
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
-
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, led => led);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
+
use work.types.all;
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
entity top_level is
|
| 9 |
port (
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
architecture rtl of top_level is
|
| 17 |
+
signal mem_req: mem_req_t;
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
component core is
|
| 20 |
port (
|
| 21 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 22 |
+
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
| 23 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 24 |
);
|
| 25 |
end component;
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
+
component mem_subsys is
|
| 28 |
+
port (
|
| 29 |
+
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 30 |
+
req: in mem_req_t;
|
| 31 |
+
);
|
| 32 |
+
end component;
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
begin
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
+
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, led => led);
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req);
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
end rtl;
|
Now implementing OP_SW in the execute stage is simple.
|
@@ -30,11 +30,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 30 |
variable v_sign: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 31 |
variable v_jump: std_logic;
|
| 32 |
variable v_jump_address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
begin
|
| 35 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 36 |
v_output := DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT;
|
| 37 |
v_output.is_active := input.is_active;
|
|
|
|
| 38 |
v_jump := '0';
|
| 39 |
v_jump_address := (others => '0');
|
| 40 |
|
|
@@ -138,7 +140,9 @@ begin
|
|
| 138 |
v_jump_address := input.operand3;
|
| 139 |
end if;
|
| 140 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 141 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 143 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 144 |
else
|
|
@@ -148,10 +152,12 @@ begin
|
|
| 148 |
v_output.destination_reg := input.destination_reg;
|
| 149 |
end if;
|
| 150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 151 |
jump <= v_jump;
|
| 152 |
jump_address <= v_jump_address(31 downto 1) & "0";
|
| 153 |
-
|
| 154 |
-
output <= v_output;
|
| 155 |
end if;
|
| 156 |
end process;
|
| 157 |
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
variable v_sign: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 31 |
variable v_jump: std_logic;
|
| 32 |
variable v_jump_address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 33 |
+
variable v_mem_req: mem_req_t;
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
begin
|
| 36 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 37 |
v_output := DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT;
|
| 38 |
v_output.is_active := input.is_active;
|
| 39 |
+
v_mem_req := DEFAULT_MEM_REQ;
|
| 40 |
v_jump := '0';
|
| 41 |
v_jump_address := (others => '0');
|
| 42 |
|
|
|
|
| 140 |
v_jump_address := input.operand3;
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 145 |
+
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 146 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 147 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 148 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 152 |
v_output.destination_reg := input.destination_reg;
|
| 153 |
end if;
|
| 154 |
|
| 155 |
+
output <= v_output;
|
| 156 |
+
|
| 157 |
+
mem_req <= v_mem_req;
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
jump <= v_jump;
|
| 160 |
jump_address <= v_jump_address(31 downto 1) & "0";
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 161 |
end if;
|
| 162 |
end process;
|
| 163 |
|
Now we need to implement the memory subsystem itself. In the spirit of "doing the simplest thing that could work", we can just make a vector of std_logic_vectors like we did for the registers. Let's make it 4KB big, which means it's 1024 words, since words consists of 4 bytes.
|
@@ -15,5 +15,17 @@ end mem_subsys;
|
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
architecture rtl of mem_subsys is
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
begin
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 19 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
architecture rtl of mem_subsys is
|
| 18 |
+
type ram_t is array (0 to 1023) of std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 19 |
+
signal ram: ram_t := (others => (others => '0'));
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
begin
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
process (clk)
|
| 24 |
+
begin
|
| 25 |
+
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 26 |
+
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 27 |
+
ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2)))) <= req.value;
|
| 28 |
+
end if;
|
| 29 |
+
end if;
|
| 30 |
+
end process;
|
| 31 |
end rtl;
|
Now, let's write a simple program that increments a counter, and uses the counter as both the address and the value to write. Since the address is in bytes but we're writing words, we'll shift the address to the left by two bits, which makes sure the address is a multiple of 4 so that our stores are aligned.
loop:
sll x2, x1, 2
sw x1, 0(x2)
addi x1, x1, 1
j loop
This assembles to
00209113
00112023
00108093
ff5ff06f
|
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ end fetch;
|
|
| 20 |
architecture rtl of fetch is
|
| 21 |
type instruction_memory_t is array(0 to 15) of std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 22 |
signal imem: instruction_memory_t := (
|
| 23 |
-
X"
|
| 24 |
X"0000006f", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000"
|
| 25 |
);
|
| 26 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
architecture rtl of fetch is
|
| 21 |
type instruction_memory_t is array(0 to 15) of std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 22 |
signal imem: instruction_memory_t := (
|
| 23 |
+
X"00112023", X"00108093", X"00209113", X"ff5ff06f", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000",
|
| 24 |
X"0000006f", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000"
|
| 25 |
);
|
| 26 |
|
|
@@ -26,6 +26,6 @@ begin
|
|
| 26 |
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 27 |
ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2)))) <= req.value;
|
| 28 |
end if;
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
end process;
|
| 31 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 27 |
ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2)))) <= req.value;
|
| 28 |
end if;
|
| 29 |
+
end if;
|
| 30 |
end process;
|
| 31 |
end rtl;
|
And... This looks good! Our memory gets filled, word by word.
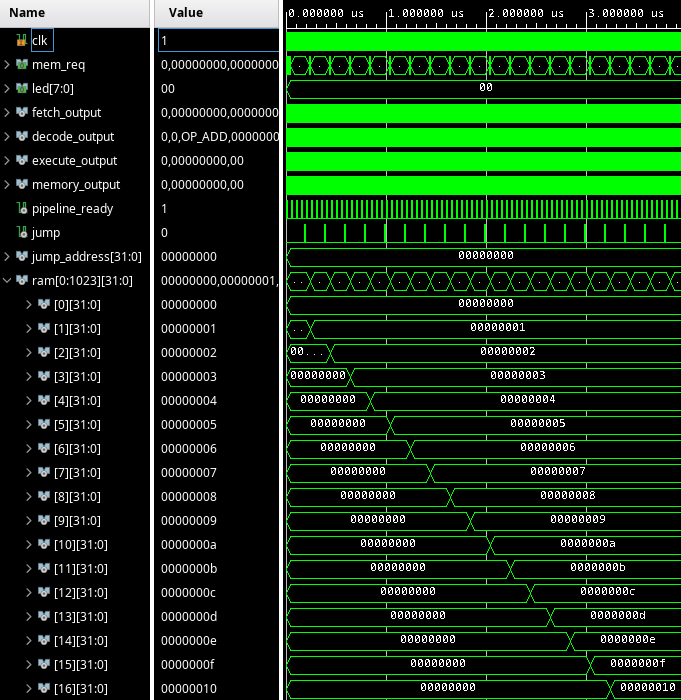
Now, I want to proceed by implementing the LW (load word) instruction. This is somewhat similar to storing a word, in that the execute stage will signal an address to the memory subsystem, and the memory subsystem will act on it.
However, the memory subsystem needs to know if it has to perform a read or a write command. So let's add a type and field for it.
|
@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ use work.types.all;
|
|
| 7 |
package constants is
|
| 8 |
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
active => '0',
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 11 |
value => (others => '0')
|
| 12 |
);
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
package constants is
|
| 8 |
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
active => '0',
|
| 10 |
+
cmd => MEM_CMD_READ,
|
| 11 |
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 12 |
value => (others => '0')
|
| 13 |
);
|
|
@@ -3,8 +3,11 @@ use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
package types is
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 7 |
active: std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 9 |
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 10 |
end record mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
package types is
|
| 6 |
+
type mem_cmd_t is (MEM_CMD_READ, MEM_CMD_WRITE);
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 9 |
active: std_logic;
|
| 10 |
+
cmd: mem_cmd_t;
|
| 11 |
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 12 |
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 13 |
end record mem_req_t;
|
Now, we still need to set the proper command in the execute stage.
|
@@ -141,6 +141,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
|
|
|
| 144 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 146 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
|
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
+
v_mem_req.cmd := MEM_CMD_WRITE;
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
We are now ready to start implementing LW. First, we add an operation for it.
|
@@ -22,6 +22,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 22 |
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
OP_BGEU,
|
| 24 |
OP_SW,
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
OP_LED
|
| 26 |
);
|
| 27 |
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
OP_BGEU,
|
| 24 |
OP_SW,
|
| 25 |
+
OP_LW,
|
| 26 |
OP_LED
|
| 27 |
);
|
| 28 |
|
We are now ready to decode LW instructions. The address computation is the same as for the SW instruction, but this time we need to set the destination register.
|
@@ -129,12 +129,17 @@ begin
|
|
| 129 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 130 |
end if;
|
| 131 |
elsif opcode = "0000011" then
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 132 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 133 |
-- TODO: LB
|
| 134 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 135 |
-- TODO: LH
|
| 136 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 137 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 138 |
elsif funct3 = "100" then
|
| 139 |
-- TODO: LBU
|
| 140 |
elsif funct3 = "101" then
|
|
|
|
| 129 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 130 |
end if;
|
| 131 |
elsif opcode = "0000011" then
|
| 132 |
+
-- load instructions
|
| 133 |
+
v_decode_output.operand1 := std_logic_vector(unsigned(reg(to_integer(unsigned(rs1)))) + unsigned(i_imm_s));
|
| 134 |
+
v_decode_output.destination_reg := rd;
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 137 |
-- TODO: LB
|
| 138 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 139 |
-- TODO: LH
|
| 140 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 141 |
+
-- LW
|
| 142 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LW;
|
| 143 |
elsif funct3 = "100" then
|
| 144 |
-- TODO: LBU
|
| 145 |
elsif funct3 = "101" then
|
Now we can tell the memory subsystem to read from the execute stage.
|
@@ -144,6 +144,10 @@ begin
|
|
| 144 |
v_mem_req.cmd := MEM_CMD_WRITE;
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 148 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 149 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 144 |
v_mem_req.cmd := MEM_CMD_WRITE;
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 148 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 149 |
+
v_mem_req.cmd := MEM_CMD_READ;
|
| 150 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 151 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 152 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 153 |
else
|
We still need to implement reading in the memory subsystem. I'll add an output named res (for "response").
|
@@ -9,7 +9,8 @@ use work.constants.all;
|
|
| 9 |
entity mem_subsys is
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
-
req: in mem_req_t
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
);
|
| 14 |
end mem_subsys;
|
| 15 |
|
|
@@ -24,7 +25,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 24 |
begin
|
| 25 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 26 |
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 27 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 28 |
end if;
|
| 29 |
end if;
|
| 30 |
end process;
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
entity mem_subsys is
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
+
req: in mem_req_t;
|
| 13 |
+
res: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0)
|
| 14 |
);
|
| 15 |
end mem_subsys;
|
| 16 |
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
begin
|
| 26 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 27 |
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 28 |
+
if req.cmd = MEM_CMD_WRITE then
|
| 29 |
+
ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2)))) <= req.value;
|
| 30 |
+
else
|
| 31 |
+
res <= ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2))));
|
| 32 |
+
end if;
|
| 33 |
+
else
|
| 34 |
+
res <= (others => '0');
|
| 35 |
end if;
|
| 36 |
end if;
|
| 37 |
end process;
|
|
@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@ end top_level;
|
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
architecture rtl of top_level is
|
| 17 |
signal mem_req: mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
component core is
|
| 20 |
port (
|
|
@@ -28,6 +29,7 @@ architecture rtl of top_level is
|
|
| 28 |
port (
|
| 29 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 30 |
req: in mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 31 |
);
|
| 32 |
end component;
|
| 33 |
|
|
@@ -35,6 +37,6 @@ begin
|
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, led => led);
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
-
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req);
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
architecture rtl of top_level is
|
| 17 |
signal mem_req: mem_req_t;
|
| 18 |
+
signal mem_res: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
component core is
|
| 21 |
port (
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
port (
|
| 30 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 31 |
req: in mem_req_t;
|
| 32 |
+
res: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0)
|
| 33 |
);
|
| 34 |
end component;
|
| 35 |
|
|
|
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, led => led);
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
+
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req, res => mem_res);
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
end rtl;
|
This output needs to be routed back to the core.
|
@@ -9,7 +9,8 @@ use work.constants.all;
|
|
| 9 |
entity mem_subsys is
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
-
req: in mem_req_t
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
);
|
| 14 |
end mem_subsys;
|
| 15 |
|
|
@@ -24,7 +25,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 24 |
begin
|
| 25 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 26 |
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 27 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 28 |
end if;
|
| 29 |
end if;
|
| 30 |
end process;
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
entity mem_subsys is
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
+
req: in mem_req_t;
|
| 13 |
+
res: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0)
|
| 14 |
);
|
| 15 |
end mem_subsys;
|
| 16 |
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
begin
|
| 26 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 27 |
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 28 |
+
if req.cmd = MEM_CMD_WRITE then
|
| 29 |
+
ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2)))) <= req.value;
|
| 30 |
+
else
|
| 31 |
+
res <= ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2))));
|
| 32 |
+
end if;
|
| 33 |
+
else
|
| 34 |
+
res <= (others => '0');
|
| 35 |
end if;
|
| 36 |
end if;
|
| 37 |
end process;
|
|
@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@ end top_level;
|
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
architecture rtl of top_level is
|
| 17 |
signal mem_req: mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
component core is
|
| 20 |
port (
|
|
@@ -28,6 +29,7 @@ architecture rtl of top_level is
|
|
| 28 |
port (
|
| 29 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 30 |
req: in mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 31 |
);
|
| 32 |
end component;
|
| 33 |
|
|
@@ -35,6 +37,6 @@ begin
|
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, led => led);
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
-
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req);
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
architecture rtl of top_level is
|
| 17 |
signal mem_req: mem_req_t;
|
| 18 |
+
signal mem_res: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
component core is
|
| 21 |
port (
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
port (
|
| 30 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 31 |
req: in mem_req_t;
|
| 32 |
+
res: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0)
|
| 33 |
);
|
| 34 |
end component;
|
| 35 |
|
|
|
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, led => led);
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
+
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req, res => mem_res);
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
end rtl;
|
Now, we want to route it back to some stage. When the execute stage writes its output, the memory stage is running (for one cycle). At the same time, the memory subsystem is also doing the read. So, the output from the read will not arrive in time for the memory stage; we can only use it in the writeback stage. So, we are not doing anything in the memory stage, except just adding a single-cycle delay to make sure the value that is read from the memory arrives in time for the writeback stage.
|
@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@ entity core is
|
|
| 12 |
port (
|
| 13 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 14 |
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 16 |
);
|
| 17 |
end core;
|
|
@@ -42,6 +43,7 @@ architecture rtl of core is
|
|
| 42 |
decode_input: in fetch_output_t;
|
| 43 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t;
|
| 44 |
write_input: in memory_output_t;
|
|
|
|
| 45 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic
|
| 46 |
);
|
| 47 |
end component;
|
|
@@ -69,7 +71,7 @@ architecture rtl of core is
|
|
| 69 |
begin
|
| 70 |
fetch_inst: fetch port map(clk => clk, pipeline_ready => pipeline_ready, jump => jump, jump_address => jump_address, output => fetch_output);
|
| 71 |
|
| 72 |
-
decode_write_inst: decode_write port map(clk => clk, decode_input => fetch_output, decode_output => decode_output, write_input => memory_output, pipeline_ready => pipeline_ready);
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
execute_inst: execute port map(clk => clk, input => decode_output, output => execute_output, mem_req => mem_req, jump => jump, jump_address => jump_address, led => led);
|
| 75 |
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
port (
|
| 13 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 14 |
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
| 15 |
+
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 16 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 17 |
);
|
| 18 |
end core;
|
|
|
|
| 43 |
decode_input: in fetch_output_t;
|
| 44 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t;
|
| 45 |
write_input: in memory_output_t;
|
| 46 |
+
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 47 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic
|
| 48 |
);
|
| 49 |
end component;
|
|
|
|
| 71 |
begin
|
| 72 |
fetch_inst: fetch port map(clk => clk, pipeline_ready => pipeline_ready, jump => jump, jump_address => jump_address, output => fetch_output);
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
+
decode_write_inst: decode_write port map(clk => clk, decode_input => fetch_output, decode_output => decode_output, write_input => memory_output, mem_res => mem_res, pipeline_ready => pipeline_ready);
|
| 75 |
|
| 76 |
execute_inst: execute port map(clk => clk, input => decode_output, output => execute_output, mem_req => mem_req, jump => jump, jump_address => jump_address, led => led);
|
| 77 |
|
|
@@ -14,6 +14,7 @@ entity decode_write is
|
|
| 14 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t := DEFAULT_DECODE_OUTPUT;
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
write_input: in memory_output_t;
|
|
|
|
| 17 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic := '1'
|
| 18 |
);
|
| 19 |
end decode_write;
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t := DEFAULT_DECODE_OUTPUT;
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
write_input: in memory_output_t;
|
| 17 |
+
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 18 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic := '1'
|
| 19 |
);
|
| 20 |
end decode_write;
|
|
@@ -21,6 +21,7 @@ architecture rtl of top_level is
|
|
| 21 |
port (
|
| 22 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 23 |
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 25 |
);
|
| 26 |
end component;
|
|
@@ -35,7 +36,7 @@ architecture rtl of top_level is
|
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
begin
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
-
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, led => led);
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req, res => mem_res);
|
| 41 |
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
port (
|
| 22 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 23 |
mem_req: out mem_req_t;
|
| 24 |
+
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 25 |
led: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)
|
| 26 |
);
|
| 27 |
end component;
|
|
|
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
begin
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
+
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk, mem_req => mem_req, mem_res => mem_res, led => led);
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
mem_subsys_inst: mem_subsys port map(clk => clk, req => mem_req, res => mem_res);
|
| 42 |
|
Now, as a last step, the execute stage needs to tell the writeback stage that it has to store the response from the memory in the destination register, instead of the result output from the execute stage. For this, I add a use_mem flag to the output of the execute stage. It needs to be routed through the memory stage, so I'll add it to the output of the memory stage as well.
|
@@ -23,12 +23,14 @@ package core_constants is
|
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
constant DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT: execute_output_t := (
|
| 25 |
is_active => '0',
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 27 |
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 28 |
);
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
constant DEFAULT_MEMORY_OUTPUT: memory_output_t := (
|
| 31 |
is_active => '0',
|
|
|
|
| 32 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 33 |
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 34 |
);
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
constant DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT: execute_output_t := (
|
| 25 |
is_active => '0',
|
| 26 |
+
use_mem => '0',
|
| 27 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 28 |
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 29 |
);
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
constant DEFAULT_MEMORY_OUTPUT: memory_output_t := (
|
| 32 |
is_active => '0',
|
| 33 |
+
use_mem => '0',
|
| 34 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 35 |
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 36 |
);
|
|
@@ -44,12 +44,14 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
type execute_output_t is record
|
| 46 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 47 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 48 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 49 |
end record execute_output_t;
|
| 50 |
|
| 51 |
type memory_output_t is record
|
| 52 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 53 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 54 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 55 |
end record memory_output_t;
|
|
|
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
type execute_output_t is record
|
| 46 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
| 47 |
+
use_mem: std_logic;
|
| 48 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 49 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 50 |
end record execute_output_t;
|
| 51 |
|
| 52 |
type memory_output_t is record
|
| 53 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
| 54 |
+
use_mem: std_logic;
|
| 55 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 56 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 57 |
end record memory_output_t;
|
Now, we need to set this flag in the execute stage whenever we perform a read.
|
@@ -145,6 +145,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
|
|
|
| 148 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 149 |
v_mem_req.cmd := MEM_CMD_READ;
|
| 150 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
|
|
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 148 |
+
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 149 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 150 |
v_mem_req.cmd := MEM_CMD_READ;
|
| 151 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
Finally, we need to update the writeback stage to actually write back the memory response when the use_mem flag is set.
|
@@ -47,7 +47,11 @@ begin
|
|
| 47 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 48 |
-- write back result if the destination register is not x0 (which always stays 0)
|
| 49 |
if write_input.destination_reg /= "00000" then
|
| 50 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
end if;
|
| 52 |
|
| 53 |
pipeline_ready <= write_input.is_active;
|
|
|
|
| 47 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 48 |
-- write back result if the destination register is not x0 (which always stays 0)
|
| 49 |
if write_input.destination_reg /= "00000" then
|
| 50 |
+
if write_input.use_mem = '1' then
|
| 51 |
+
reg(to_integer(unsigned(write_input.destination_reg))) <= mem_res;
|
| 52 |
+
else
|
| 53 |
+
reg(to_integer(unsigned(write_input.destination_reg))) <= write_input.result;
|
| 54 |
+
end if;
|
| 55 |
end if;
|
| 56 |
|
| 57 |
pipeline_ready <= write_input.is_active;
|
That's it, I guess? We can adapt our program from before by adding a load of the same address immediately after the store.
loop:
sll x2, x1, 2
sw x1, 0(x2)
lw x5, 0(x2)
addi x1, x1, 1
j loop
This assembles to
00209113
00112023
00012283
00108093
ff1ff06f
So we'll put this in the instruction memory.
|
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ end fetch;
|
|
| 20 |
architecture rtl of fetch is
|
| 21 |
type instruction_memory_t is array(0 to 15) of std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 22 |
signal imem: instruction_memory_t := (
|
| 23 |
-
X"
|
| 24 |
X"0000006f", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000"
|
| 25 |
);
|
| 26 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
architecture rtl of fetch is
|
| 21 |
type instruction_memory_t is array(0 to 15) of std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 22 |
signal imem: instruction_memory_t := (
|
| 23 |
+
X"00209113", X"00112023", X"00012283", X"00108093", X"ff1ff06f", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000",
|
| 24 |
X"0000006f", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000"
|
| 25 |
);
|
| 26 |
|
When we simulate this... It doesn't work?
After tracing the signals, it becomes obvious we forgot to pass the use_mem flag in the memory stage. We can just update it to also copy this flag:
|
@@ -22,6 +22,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 22 |
begin
|
| 23 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 24 |
output.is_active <= input.is_active;
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
output.result <= input.result;
|
| 26 |
output.destination_reg <= input.destination_reg;
|
| 27 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
begin
|
| 23 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 24 |
output.is_active <= input.is_active;
|
| 25 |
+
output.use_mem <= input.use_mem;
|
| 26 |
output.result <= input.result;
|
| 27 |
output.destination_reg <= input.destination_reg;
|
| 28 |
end if;
|
Actually, since the memory stage does nothing, we can just remove the memory_output_t, since it is exactly the same as execute_output_t. So let's do a bit of cleanup and remove the memory_output_t and associated constants, and replace it by execute_output_t whenever it's used.
|
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
|
| 7 |
<Project Product="Vivado" Version="7" Minor="70" Path="/home/ruben/projects/cpucourse2/cpu/cpu.xpr">
|
| 8 |
<DefaultLaunch Dir="$PRUNDIR"/>
|
| 9 |
<Configuration>
|
| 10 |
-
<Option Name="Id" Val="
|
| 11 |
<Option Name="Part" Val="xc7a50tfgg484-1"/>
|
| 12 |
<Option Name="CompiledLibDir" Val="$PCACHEDIR/compile_simlib"/>
|
| 13 |
<Option Name="CompiledLibDirXSim" Val=""/>
|
|
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@
|
|
| 58 |
<Option Name="IPUserFilesDir" Val="$PIPUSERFILESDIR"/>
|
| 59 |
<Option Name="IPStaticSourceDir" Val="$PIPUSERFILESDIR/ipstatic"/>
|
| 60 |
<Option Name="EnableBDX" Val="FALSE"/>
|
| 61 |
-
<Option Name="WTXSimLaunchSim" Val="
|
| 62 |
<Option Name="WTModelSimLaunchSim" Val="0"/>
|
| 63 |
<Option Name="WTQuestaLaunchSim" Val="0"/>
|
| 64 |
<Option Name="WTIesLaunchSim" Val="0"/>
|
|
@@ -89,55 +89,73 @@
|
|
| 89 |
<FileSets Version="1" Minor="32">
|
| 90 |
<FileSet Name="sources_1" Type="DesignSrcs" RelSrcDir="$PSRCDIR/sources_1" RelGenDir="$PGENDIR/sources_1">
|
| 91 |
<Filter Type="Srcs"/>
|
| 92 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/
|
| 93 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 94 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 95 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 96 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 97 |
</File>
|
| 98 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/
|
| 99 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 100 |
-
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 101 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 102 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 103 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 104 |
</File>
|
| 105 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/
|
| 106 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 107 |
-
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 108 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 109 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 110 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 111 |
</File>
|
| 112 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/
|
| 113 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 114 |
-
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 115 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 116 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 117 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 118 |
</File>
|
| 119 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core
|
| 120 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 121 |
-
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 122 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 123 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 124 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 125 |
</File>
|
| 126 |
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/decode_write.vhd">
|
| 127 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 128 |
-
<Attr Name="
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 129 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 130 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 131 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 132 |
</File>
|
| 133 |
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/fetch.vhd">
|
| 134 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 135 |
-
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 136 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 137 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 138 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 139 |
</File>
|
| 140 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 141 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 142 |
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 143 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
|
@@ -163,13 +181,13 @@
|
|
| 163 |
</FileSet>
|
| 164 |
<FileSet Name="sim_1" Type="SimulationSrcs" RelSrcDir="$PSRCDIR/sim_1" RelGenDir="$PGENDIR/sim_1">
|
| 165 |
<Filter Type="Srcs"/>
|
| 166 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/sim/
|
| 167 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 168 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 169 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 170 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 171 |
</File>
|
| 172 |
-
<File Path="$PPRDIR/sim/
|
| 173 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 174 |
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 175 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
|
@@ -178,9 +196,8 @@
|
|
| 178 |
</File>
|
| 179 |
<Config>
|
| 180 |
<Option Name="DesignMode" Val="RTL"/>
|
| 181 |
-
<Option Name="TopModule" Val="
|
| 182 |
<Option Name="TopLib" Val="xil_defaultlib"/>
|
| 183 |
-
<Option Name="TopAutoSet" Val="TRUE"/>
|
| 184 |
<Option Name="TransportPathDelay" Val="0"/>
|
| 185 |
<Option Name="TransportIntDelay" Val="0"/>
|
| 186 |
<Option Name="SelectedSimModel" Val="rtl"/>
|
|
@@ -224,11 +241,12 @@
|
|
| 224 |
</Simulator>
|
| 225 |
</Simulators>
|
| 226 |
<Runs Version="1" Minor="22">
|
| 227 |
-
<Run Id="synth_1" Type="Ft3:Synth" SrcSet="sources_1" Part="xc7a50tfgg484-1" ConstrsSet="constrs_1" Description="Vivado Synthesis Defaults" AutoIncrementalCheckpoint="true" WriteIncrSynthDcp="false" State="current" IncludeInArchive="true" IsChild="false" AutoIncrementalDir="$PSRCDIR/utils_1/imports/synth_1" AutoRQSDir="$PSRCDIR/utils_1/imports/synth_1" ParallelReportGen="true">
|
| 228 |
<Strategy Version="1" Minor="2">
|
| 229 |
<StratHandle Name="Vivado Synthesis Defaults" Flow="Vivado Synthesis 2025"/>
|
| 230 |
<Step Id="synth_design"/>
|
| 231 |
</Strategy>
|
|
|
|
| 232 |
<ReportStrategy Name="Vivado Synthesis Default Reports" Flow="Vivado Synthesis 2025"/>
|
| 233 |
<Report Name="ROUTE_DESIGN.REPORT_METHODOLOGY" Enabled="1"/>
|
| 234 |
<RQSFiles/>
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
<Project Product="Vivado" Version="7" Minor="70" Path="/home/ruben/projects/cpucourse2/cpu/cpu.xpr">
|
| 8 |
<DefaultLaunch Dir="$PRUNDIR"/>
|
| 9 |
<Configuration>
|
| 10 |
+
<Option Name="Id" Val="4a9cfec0f8464be581feae96340e3ce2"/>
|
| 11 |
<Option Name="Part" Val="xc7a50tfgg484-1"/>
|
| 12 |
<Option Name="CompiledLibDir" Val="$PCACHEDIR/compile_simlib"/>
|
| 13 |
<Option Name="CompiledLibDirXSim" Val=""/>
|
|
|
|
| 58 |
<Option Name="IPUserFilesDir" Val="$PIPUSERFILESDIR"/>
|
| 59 |
<Option Name="IPStaticSourceDir" Val="$PIPUSERFILESDIR/ipstatic"/>
|
| 60 |
<Option Name="EnableBDX" Val="FALSE"/>
|
| 61 |
+
<Option Name="WTXSimLaunchSim" Val="5"/>
|
| 62 |
<Option Name="WTModelSimLaunchSim" Val="0"/>
|
| 63 |
<Option Name="WTQuestaLaunchSim" Val="0"/>
|
| 64 |
<Option Name="WTIesLaunchSim" Val="0"/>
|
|
|
|
| 89 |
<FileSets Version="1" Minor="32">
|
| 90 |
<FileSet Name="sources_1" Type="DesignSrcs" RelSrcDir="$PSRCDIR/sources_1" RelGenDir="$PGENDIR/sources_1">
|
| 91 |
<Filter Type="Srcs"/>
|
| 92 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/types.vhd">
|
| 93 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 94 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 95 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 96 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 97 |
</File>
|
| 98 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/constants.vhd">
|
| 99 |
<FileInfo>
|
|
|
|
| 100 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 101 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 102 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 103 |
</File>
|
| 104 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/types.vhd">
|
| 105 |
<FileInfo>
|
|
|
|
| 106 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 107 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 108 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 109 |
</File>
|
| 110 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/constants.vhd">
|
| 111 |
<FileInfo>
|
|
|
|
| 112 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 113 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 114 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 115 |
</File>
|
| 116 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core.vhd">
|
| 117 |
<FileInfo>
|
|
|
|
| 118 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 119 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 120 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 121 |
</File>
|
| 122 |
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/decode_write.vhd">
|
| 123 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 124 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 125 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 126 |
+
</FileInfo>
|
| 127 |
+
</File>
|
| 128 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/execute.vhd">
|
| 129 |
+
<FileInfo>
|
| 130 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 131 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 132 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 133 |
</File>
|
| 134 |
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/fetch.vhd">
|
| 135 |
<FileInfo>
|
|
|
|
| 136 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 137 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 138 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 139 |
</File>
|
| 140 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/mem_subsys.vhd">
|
| 141 |
+
<FileInfo>
|
| 142 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 143 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 144 |
+
</FileInfo>
|
| 145 |
+
</File>
|
| 146 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/core/memory.vhd">
|
| 147 |
+
<FileInfo>
|
| 148 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 149 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 150 |
+
</FileInfo>
|
| 151 |
+
</File>
|
| 152 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/top_level.vhd">
|
| 153 |
+
<FileInfo>
|
| 154 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 155 |
+
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 156 |
+
</FileInfo>
|
| 157 |
+
</File>
|
| 158 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/src/bram.vhd">
|
| 159 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 160 |
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 161 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
|
|
|
| 181 |
</FileSet>
|
| 182 |
<FileSet Name="sim_1" Type="SimulationSrcs" RelSrcDir="$PSRCDIR/sim_1" RelGenDir="$PGENDIR/sim_1">
|
| 183 |
<Filter Type="Srcs"/>
|
| 184 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/sim/top_level_tb.vhd">
|
| 185 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 186 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
| 187 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="simulation"/>
|
| 188 |
</FileInfo>
|
| 189 |
</File>
|
| 190 |
+
<File Path="$PPRDIR/sim/core_tb.vhd">
|
| 191 |
<FileInfo>
|
| 192 |
<Attr Name="AutoDisabled" Val="1"/>
|
| 193 |
<Attr Name="UsedIn" Val="synthesis"/>
|
|
|
|
| 196 |
</File>
|
| 197 |
<Config>
|
| 198 |
<Option Name="DesignMode" Val="RTL"/>
|
| 199 |
+
<Option Name="TopModule" Val="top_level_tb"/>
|
| 200 |
<Option Name="TopLib" Val="xil_defaultlib"/>
|
|
|
|
| 201 |
<Option Name="TransportPathDelay" Val="0"/>
|
| 202 |
<Option Name="TransportIntDelay" Val="0"/>
|
| 203 |
<Option Name="SelectedSimModel" Val="rtl"/>
|
|
|
|
| 241 |
</Simulator>
|
| 242 |
</Simulators>
|
| 243 |
<Runs Version="1" Minor="22">
|
| 244 |
+
<Run Id="synth_1" Type="Ft3:Synth" SrcSet="sources_1" Part="xc7a50tfgg484-1" ConstrsSet="constrs_1" Description="Vivado Synthesis Defaults" AutoIncrementalCheckpoint="true" WriteIncrSynthDcp="false" State="current" Dir="$PRUNDIR/synth_1" IncludeInArchive="true" IsChild="false" AutoIncrementalDir="$PSRCDIR/utils_1/imports/synth_1" AutoRQSDir="$PSRCDIR/utils_1/imports/synth_1" ParallelReportGen="true">
|
| 245 |
<Strategy Version="1" Minor="2">
|
| 246 |
<StratHandle Name="Vivado Synthesis Defaults" Flow="Vivado Synthesis 2025"/>
|
| 247 |
<Step Id="synth_design"/>
|
| 248 |
</Strategy>
|
| 249 |
+
<GeneratedRun Dir="$PRUNDIR" File="gen_run.xml"/>
|
| 250 |
<ReportStrategy Name="Vivado Synthesis Default Reports" Flow="Vivado Synthesis 2025"/>
|
| 251 |
<Report Name="ROUTE_DESIGN.REPORT_METHODOLOGY" Enabled="1"/>
|
| 252 |
<RQSFiles/>
|
|
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ architecture rtl of core is
|
|
| 22 |
signal fetch_output: fetch_output_t;
|
| 23 |
signal decode_output: decode_output_t;
|
| 24 |
signal execute_output: execute_output_t;
|
| 25 |
-
signal memory_output:
|
| 26 |
signal pipeline_ready: std_logic;
|
| 27 |
signal jump: std_logic;
|
| 28 |
signal jump_address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
|
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ architecture rtl of core is
|
|
| 42 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 43 |
decode_input: in fetch_output_t;
|
| 44 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t;
|
| 45 |
-
write_input: in
|
| 46 |
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 47 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic
|
| 48 |
);
|
|
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ architecture rtl of core is
|
|
| 64 |
port (
|
| 65 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 66 |
input: in execute_output_t;
|
| 67 |
-
output: out
|
| 68 |
);
|
| 69 |
end component;
|
| 70 |
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
signal fetch_output: fetch_output_t;
|
| 23 |
signal decode_output: decode_output_t;
|
| 24 |
signal execute_output: execute_output_t;
|
| 25 |
+
signal memory_output: execute_output_t;
|
| 26 |
signal pipeline_ready: std_logic;
|
| 27 |
signal jump: std_logic;
|
| 28 |
signal jump_address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 42 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 43 |
decode_input: in fetch_output_t;
|
| 44 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t;
|
| 45 |
+
write_input: in execute_output_t;
|
| 46 |
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 47 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic
|
| 48 |
);
|
|
|
|
| 64 |
port (
|
| 65 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 66 |
input: in execute_output_t;
|
| 67 |
+
output: out execute_output_t
|
| 68 |
);
|
| 69 |
end component;
|
| 70 |
|
|
@@ -27,11 +27,4 @@ package core_constants is
|
|
| 27 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 28 |
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 29 |
);
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
constant DEFAULT_MEMORY_OUTPUT: memory_output_t := (
|
| 32 |
-
is_active => '0',
|
| 33 |
-
use_mem => '0',
|
| 34 |
-
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 35 |
-
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 36 |
-
);
|
| 37 |
end package core_constants;
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 28 |
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
| 29 |
);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
end package core_constants;
|
|
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ entity decode_write is
|
|
| 13 |
decode_input: in fetch_output_t;
|
| 14 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t := DEFAULT_DECODE_OUTPUT;
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
-
write_input: in
|
| 17 |
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 18 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic := '1'
|
| 19 |
);
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
decode_input: in fetch_output_t;
|
| 14 |
decode_output: out decode_output_t := DEFAULT_DECODE_OUTPUT;
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
+
write_input: in execute_output_t;
|
| 17 |
mem_res: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 18 |
pipeline_ready: out std_logic := '1'
|
| 19 |
);
|
|
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ entity memory is
|
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
input: in execute_output_t;
|
| 13 |
-
output: out
|
| 14 |
);
|
| 15 |
end memory;
|
| 16 |
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
port (
|
| 11 |
clk: in std_logic;
|
| 12 |
input: in execute_output_t;
|
| 13 |
+
output: out execute_output_t := DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT
|
| 14 |
);
|
| 15 |
end memory;
|
| 16 |
|
|
@@ -48,11 +48,4 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 48 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 49 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 50 |
end record execute_output_t;
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
type memory_output_t is record
|
| 53 |
-
is_active: std_logic;
|
| 54 |
-
use_mem: std_logic;
|
| 55 |
-
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 56 |
-
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 57 |
-
end record memory_output_t;
|
| 58 |
end package core_types;
|
|
|
|
| 48 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 49 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 50 |
end record execute_output_t;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
end package core_types;
|
The memory stage can now be simplified.
|
@@ -21,10 +21,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 21 |
process (clk)
|
| 22 |
begin
|
| 23 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 24 |
-
output
|
| 25 |
-
output.use_mem <= input.use_mem;
|
| 26 |
-
output.result <= input.result;
|
| 27 |
-
output.destination_reg <= input.destination_reg;
|
| 28 |
end if;
|
| 29 |
end process;
|
| 30 |
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
process (clk)
|
| 22 |
begin
|
| 23 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 24 |
+
output <= input;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
end if;
|
| 26 |
end process;
|
| 27 |
|
We now want to simulate this. From now on, we'll always want to use top_level_tb.vhd, because just the core is not enough. We might as well delete it to avoid confusion.
|
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
library ieee;
|
| 2 |
-
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
-
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
entity core_tb is
|
| 7 |
-
end core_tb;
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
architecture behavioral of core_tb is
|
| 11 |
-
constant clk_period: time := 10 ns;
|
| 12 |
-
signal clk: std_logic := '1';
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
component core is
|
| 15 |
-
port (
|
| 16 |
-
clk: in std_logic
|
| 17 |
-
);
|
| 18 |
-
end component;
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
begin
|
| 21 |
-
clk_process :process
|
| 22 |
-
begin
|
| 23 |
-
clk <= '1';
|
| 24 |
-
wait for clk_period / 2;
|
| 25 |
-
clk <= '0';
|
| 26 |
-
wait for clk_period / 2;
|
| 27 |
-
end process;
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
core_inst: core port map(clk => clk);
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
end behavioral;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If we now simulate for 500ns and watch the x5 register, we can see the successive values getting loaded.
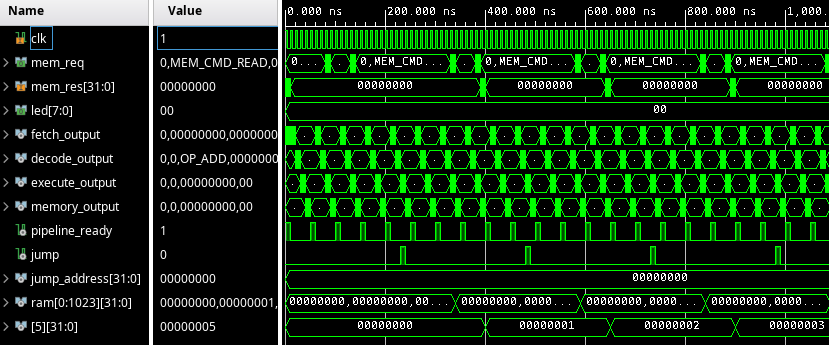
Next, we're going to implement byte and halfword reads, which require us to write only some of the bytes, instead of always the whole 32-bit word.
To support this, I am going to copy and edit some code from AMD's docs, that is supposed to infer a block RAM. This code supports a "write enable" input, which I want to use.
|
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
library ieee;
|
| 2 |
+
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
|
| 3 |
+
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
entity bram is
|
| 6 |
+
generic(
|
| 7 |
+
SIZE: integer := 1024;
|
| 8 |
+
ADDR_WIDTH: integer := 10;
|
| 9 |
+
COL_WIDTH: integer := 8;
|
| 10 |
+
NB_COL: integer := 4
|
| 11 |
+
);
|
| 12 |
+
port(
|
| 13 |
+
clka: in std_logic;
|
| 14 |
+
ena: in std_logic;
|
| 15 |
+
wea: in std_logic_vector(NB_COL - 1 downto 0);
|
| 16 |
+
addra: in std_logic_vector(ADDR_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 17 |
+
dia: in std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 18 |
+
doa: out std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0)
|
| 19 |
+
-- clkb: in std_logic;
|
| 20 |
+
-- enb: in std_logic;
|
| 21 |
+
-- web: in std_logic_vector(NB_COL - 1 downto 0);
|
| 22 |
+
-- addrb: in std_logic_vector(ADDR_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 23 |
+
-- dib: in std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 24 |
+
-- dob: out std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0)
|
| 25 |
+
);
|
| 26 |
+
end bram;
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
architecture rtl of bram is
|
| 29 |
+
type ram_type is array (0 to SIZE - 1) of std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 30 |
+
-- shared variable RAM: ram_type := (others => (others => '0'));
|
| 31 |
+
signal RAM: ram_type := (others => (others => '0'));
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
begin
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
-- port A
|
| 36 |
+
process(clka)
|
| 37 |
+
begin
|
| 38 |
+
if rising_edge(clka) then
|
| 39 |
+
if ena = '1' then
|
| 40 |
+
for i in 0 to NB_COL - 1 loop
|
| 41 |
+
if wea(i) = '1' then
|
| 42 |
+
RAM(conv_integer(addra))((i + 1) * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto i * COL_WIDTH) <= dia((i + 1) * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto i * COL_WIDTH);
|
| 43 |
+
end if;
|
| 44 |
+
end loop;
|
| 45 |
+
doa <= RAM(conv_integer(addra));
|
| 46 |
+
end if;
|
| 47 |
+
end if;
|
| 48 |
+
end process;
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
-- port B
|
| 51 |
+
-- process(clkb)
|
| 52 |
+
-- begin
|
| 53 |
+
-- if rising_edge(clkb) then
|
| 54 |
+
-- if enb = '1' then
|
| 55 |
+
-- for i in 0 to NB_COL - 1 loop
|
| 56 |
+
-- if web(i) = '1' then
|
| 57 |
+
-- RAM(conv_integer(addrb))((i + 1) * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto i * COL_WIDTH) := dib((i + 1) * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto i * COL_WIDTH);
|
| 58 |
+
-- end if;
|
| 59 |
+
-- end loop;
|
| 60 |
+
-- dob <= RAM(conv_integer(addrb));
|
| 61 |
+
-- end if;
|
| 62 |
+
-- end if;
|
| 63 |
+
-- end process;
|
| 64 |
+
end rtl;
|
Now, we'll hook up the mem_subsys code to use this bram.
|
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ use work.types.all;
|
|
| 7 |
package constants is
|
| 8 |
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
active => '0',
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 12 |
value => (others => '0')
|
| 13 |
);
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
package constants is
|
| 8 |
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
active => '0',
|
| 10 |
+
write => '0',
|
| 11 |
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 12 |
value => (others => '0')
|
| 13 |
);
|
|
@@ -141,13 +141,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
-
v_mem_req.
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 148 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 149 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 150 |
-
v_mem_req.
|
| 151 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 152 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 153 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
+
v_mem_req.write := '1';
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 148 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 149 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 150 |
+
v_mem_req.write := '0';
|
| 151 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 152 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 153 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
|
@@ -16,23 +16,24 @@ end mem_subsys;
|
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
architecture rtl of mem_subsys is
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
begin
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
-
process (clk)
|
| 25 |
-
begin
|
| 26 |
-
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 27 |
-
if req.active = '1' then
|
| 28 |
-
if req.cmd = MEM_CMD_WRITE then
|
| 29 |
-
ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2)))) <= req.value;
|
| 30 |
-
else
|
| 31 |
-
res <= ram(to_integer(unsigned(req.address(11 downto 2))));
|
| 32 |
-
end if;
|
| 33 |
-
else
|
| 34 |
-
res <= (others => '0');
|
| 35 |
-
end if;
|
| 36 |
-
end if;
|
| 37 |
-
end process;
|
| 38 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
architecture rtl of mem_subsys is
|
| 19 |
+
component bram is
|
| 20 |
+
generic(
|
| 21 |
+
SIZE: integer := 1024;
|
| 22 |
+
ADDR_WIDTH: integer := 10;
|
| 23 |
+
COL_WIDTH: integer := 8;
|
| 24 |
+
NB_COL: integer := 4
|
| 25 |
+
);
|
| 26 |
+
port(
|
| 27 |
+
clka: in std_logic;
|
| 28 |
+
ena: in std_logic;
|
| 29 |
+
wea: in std_logic_vector(NB_COL - 1 downto 0);
|
| 30 |
+
addra: in std_logic_vector(ADDR_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 31 |
+
dia: in std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0);
|
| 32 |
+
doa: out std_logic_vector(NB_COL * COL_WIDTH - 1 downto 0)
|
| 33 |
+
);
|
| 34 |
+
end component;
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
begin
|
| 37 |
+
bram_inst: bram port map(clka => clk, ena => req.active, wea => (others => req.write), addra => req.address(11 downto 2), dia => req.value, doa => res);
|
| 38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 39 |
end rtl;
|
|
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ package types is
|
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 9 |
active: std_logic;
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 12 |
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 13 |
end record mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 9 |
active: std_logic;
|
| 10 |
+
write: std_logic;
|
| 11 |
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 12 |
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 13 |
end record mem_req_t;
|
In simulation we see that our memory subsystem works just as before. However, we now have a wea signal that we can use to implement writes that only write some bytes. We want to pass this directly from the execute stage so that we can implement halfword- and byte-sized loads and stores.
|
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ use work.types.all;
|
|
| 7 |
package constants is
|
| 8 |
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
active => '0',
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 12 |
value => (others => '0')
|
| 13 |
);
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
package constants is
|
| 8 |
constant DEFAULT_MEM_REQ: mem_req_t := (
|
| 9 |
active => '0',
|
| 10 |
+
write_enable => "0000",
|
| 11 |
address => (others => '0'),
|
| 12 |
value => (others => '0')
|
| 13 |
);
|
|
@@ -141,13 +141,12 @@ begin
|
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
-
v_mem_req.
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 148 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 149 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 150 |
-
v_mem_req.write := '0';
|
| 151 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 152 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 153 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
| 145 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 146 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 147 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 148 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 149 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
|
|
|
| 150 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 151 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 152 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
|
@@ -34,6 +34,6 @@ architecture rtl of mem_subsys is
|
|
| 34 |
end component;
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
begin
|
| 37 |
-
bram_inst: bram port map(clka => clk, ena => req.active, wea =>
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
end rtl;
|
|
|
|
| 34 |
end component;
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
begin
|
| 37 |
+
bram_inst: bram port map(clka => clk, ena => req.active, wea => req.write_enable, addra => req.address(11 downto 2), dia => req.value, doa => res);
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
end rtl;
|
|
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ package types is
|
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 9 |
active: std_logic;
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 12 |
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 13 |
end record mem_req_t;
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
type mem_req_t is record
|
| 9 |
active: std_logic;
|
| 10 |
+
write_enable: std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
|
| 11 |
address: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 12 |
value: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 13 |
end record mem_req_t;
|
Now, let's first focus on writing, and in particular, the SB instruction. Since we store words as-is, and RISC-V (like most modern systems) is little-endian, we have to make sure that byte writes that are to an address aligned to 4 bytes end up in the least significant byte of the word. Likewise, byte writes to an address that ends in 01 end up in bits 15 down to 8, writes to an address that ends in 10 end up in bits 23 down to 16, and writes to an address ending in 11 end up in bits 31 down to 24.
All, in all, we get the following change.
|
@@ -158,7 +158,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 158 |
v_decode_output.operand2 := reg(to_integer(unsigned(rs2)));
|
| 159 |
|
| 160 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 161 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 162 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 163 |
-- TODO: SH
|
| 164 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
|
|
|
| 158 |
v_decode_output.operand2 := reg(to_integer(unsigned(rs2)));
|
| 159 |
|
| 160 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 161 |
+
-- SB
|
| 162 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SB;
|
| 163 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 164 |
-- TODO: SH
|
| 165 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
|
@@ -139,6 +139,23 @@ begin
|
|
| 139 |
v_jump := '1';
|
| 140 |
v_jump_address := input.operand3;
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 142 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 143 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
|
|
|
| 139 |
v_jump := '1';
|
| 140 |
v_jump_address := input.operand3;
|
| 141 |
end if;
|
| 142 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_SB then
|
| 143 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 144 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 145 |
+
|
| 146 |
+
if input.operand1(1 downto 0) = "00" then
|
| 147 |
+
v_mem_req.value := x"000000" & input.operand2(7 downto 0);
|
| 148 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "0001";
|
| 149 |
+
elsif input.operand1(1 downto 0) = "01" then
|
| 150 |
+
v_mem_req.value := x"0000" & input.operand2(7 downto 0) & x"00";
|
| 151 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "0010";
|
| 152 |
+
elsif input.operand1(1 downto 0) = "10" then
|
| 153 |
+
v_mem_req.value := x"00" & input.operand2(7 downto 0) & x"0000";
|
| 154 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "0100";
|
| 155 |
+
else
|
| 156 |
+
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2(7 downto 0) & x"000000";
|
| 157 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1000";
|
| 158 |
+
end if;
|
| 159 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 160 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 161 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
|
@@ -21,6 +21,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 21 |
OP_BGE,
|
| 22 |
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
OP_BGEU,
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
OP_SW,
|
| 25 |
OP_LW,
|
| 26 |
OP_LED
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
OP_BGE,
|
| 22 |
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
OP_BGEU,
|
| 24 |
+
OP_SB,
|
| 25 |
OP_SW,
|
| 26 |
OP_LW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LED
|
The SH instruction is very similar.
|
@@ -161,7 +161,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 161 |
-- SB
|
| 162 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SB;
|
| 163 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 164 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 165 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 166 |
-- SW
|
| 167 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SW;
|
|
|
|
| 161 |
-- SB
|
| 162 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SB;
|
| 163 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 164 |
+
-- SH
|
| 165 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SH;
|
| 166 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 167 |
-- SW
|
| 168 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_SW;
|
|
@@ -156,6 +156,17 @@ begin
|
|
| 156 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2(7 downto 0) & x"000000";
|
| 157 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1000";
|
| 158 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 159 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 160 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 161 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
|
|
|
| 156 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2(7 downto 0) & x"000000";
|
| 157 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1000";
|
| 158 |
end if;
|
| 159 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_SH then
|
| 160 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 161 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
if input.operand1(1 downto 0) = "00" then
|
| 164 |
+
v_mem_req.value := x"0000" & input.operand2(15 downto 0);
|
| 165 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "0011";
|
| 166 |
+
else
|
| 167 |
+
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2(15 downto 0) & x"0000";
|
| 168 |
+
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1100";
|
| 169 |
+
end if;
|
| 170 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 171 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 172 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
|
@@ -22,6 +22,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 22 |
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
OP_BGEU,
|
| 24 |
OP_SB,
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
OP_SW,
|
| 26 |
OP_LW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LED
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
OP_BLTU,
|
| 23 |
OP_BGEU,
|
| 24 |
OP_SB,
|
| 25 |
+
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LW,
|
| 28 |
OP_LED
|
Reading of bytes and halfwords is a lot trickier. We made it so that the response from the memory only arrives in the writeback stage. This is simple when we can store the word in a register without changes, but for the LBU and LHU instructions we need to "pad" the bytes or halfwords with some zeros, and for LB and LH instructions we even need to do sign extension.
So, in addition to the use_mem flag, the execute stage also needs to pass:
- The size of the memory read
- If the memory read needs to be sign-extended
- The lower two bits of the address (reads are always word-sized and we need to determine which bits to grab)
|
@@ -23,8 +23,11 @@ package core_constants is
|
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
constant DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT: execute_output_t := (
|
| 25 |
is_active => '0',
|
| 26 |
-
use_mem => '0',
|
| 27 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 28 |
-
destination_reg => (others => '0')
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
);
|
| 30 |
end package core_constants;
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
constant DEFAULT_EXECUTE_OUTPUT: execute_output_t := (
|
| 25 |
is_active => '0',
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
result => (others => '0'),
|
| 27 |
+
destination_reg => (others => '0'),
|
| 28 |
+
use_mem => '0',
|
| 29 |
+
mem_sign_extend => '0',
|
| 30 |
+
mem_size => SIZE_WORD,
|
| 31 |
+
mem_addr => "00"
|
| 32 |
);
|
| 33 |
end package core_constants;
|
|
@@ -44,10 +44,16 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 44 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 45 |
end record decode_output_t;
|
| 46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 47 |
type execute_output_t is record
|
| 48 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
| 49 |
-
use_mem: std_logic;
|
| 50 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 51 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 52 |
end record execute_output_t;
|
| 53 |
end package core_types;
|
|
|
|
| 44 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 45 |
end record decode_output_t;
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
+
type read_size_t is (SIZE_WORD, SIZE_HALFWORD, SIZE_BYTE);
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
type execute_output_t is record
|
| 50 |
is_active: std_logic;
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 52 |
destination_reg: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
use_mem: std_logic;
|
| 55 |
+
mem_sign_extend: std_logic;
|
| 56 |
+
mem_size: read_size_t;
|
| 57 |
+
mem_addr: std_logic_vector(1 downto 0);
|
| 58 |
end record execute_output_t;
|
| 59 |
end package core_types;
|
Let's now update the implementation of OP_LW to use these extra fields.
|
@@ -43,12 +43,25 @@ begin
|
|
| 43 |
variable u_imm: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
variable v_decode_output: decode_output_t;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 46 |
begin
|
| 47 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 48 |
-- write back result if the destination register is not x0 (which always stays 0)
|
| 49 |
if write_input.destination_reg /= "00000" then
|
| 50 |
if write_input.use_mem = '1' then
|
| 51 |
-
reg(to_integer(unsigned(write_input.destination_reg))) <=
|
| 52 |
else
|
| 53 |
reg(to_integer(unsigned(write_input.destination_reg))) <= write_input.result;
|
| 54 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
| 43 |
variable u_imm: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
variable v_decode_output: decode_output_t;
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
variable v_mem_result: std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 48 |
begin
|
| 49 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 50 |
+
-- handle endianness of memory reads
|
| 51 |
+
if write_input.mem_size = SIZE_BYTE then
|
| 52 |
+
-- TODO
|
| 53 |
+
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 54 |
+
-- TODO
|
| 55 |
+
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
| 56 |
+
v_mem_result := mem_res;
|
| 57 |
+
else
|
| 58 |
+
assert false report "Unhandled memory read size in writeback stage" severity failure;
|
| 59 |
+
end if;
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
-- write back result if the destination register is not x0 (which always stays 0)
|
| 62 |
if write_input.destination_reg /= "00000" then
|
| 63 |
if write_input.use_mem = '1' then
|
| 64 |
+
reg(to_integer(unsigned(write_input.destination_reg))) <= v_mem_result;
|
| 65 |
else
|
| 66 |
reg(to_integer(unsigned(write_input.destination_reg))) <= write_input.result;
|
| 67 |
end if;
|
|
@@ -174,6 +174,10 @@ begin
|
|
| 174 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 175 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 176 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 177 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 178 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 179 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
|
|
| 174 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 175 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LW then
|
| 176 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 177 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_WORD;
|
| 178 |
+
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 179 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 180 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 181 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 182 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 183 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
Now we can implement LBU.
|
@@ -49,7 +49,17 @@ begin
|
|
| 49 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 50 |
-- handle endianness of memory reads
|
| 51 |
if write_input.mem_size = SIZE_BYTE then
|
| 52 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 53 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 54 |
-- TODO
|
| 55 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
|
@@ -159,7 +169,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 159 |
-- LW
|
| 160 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LW;
|
| 161 |
elsif funct3 = "100" then
|
| 162 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 163 |
elsif funct3 = "101" then
|
| 164 |
-- TODO: LHU
|
| 165 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 49 |
if rising_edge(clk) then
|
| 50 |
-- handle endianness of memory reads
|
| 51 |
if write_input.mem_size = SIZE_BYTE then
|
| 52 |
+
if write_input.mem_addr = "00" then
|
| 53 |
+
v_mem_result(7 downto 0) := mem_res(7 downto 0);
|
| 54 |
+
elsif write_input.mem_addr = "01" then
|
| 55 |
+
v_mem_result(7 downto 0) := mem_res(15 downto 8);
|
| 56 |
+
elsif write_input.mem_addr = "10" then
|
| 57 |
+
v_mem_result(7 downto 0) := mem_res(23 downto 16);
|
| 58 |
+
else
|
| 59 |
+
v_mem_result(7 downto 0) := mem_res(31 downto 24);
|
| 60 |
+
end if;
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
v_mem_result(31 downto 8) := (others => '0');
|
| 63 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 64 |
-- TODO
|
| 65 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
|
|
|
| 169 |
-- LW
|
| 170 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LW;
|
| 171 |
elsif funct3 = "100" then
|
| 172 |
+
-- LBU
|
| 173 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LBU;
|
| 174 |
elsif funct3 = "101" then
|
| 175 |
-- TODO: LHU
|
| 176 |
else
|
|
@@ -178,6 +178,12 @@ begin
|
|
| 178 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 179 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 180 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 181 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 182 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 183 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
|
|
| 178 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 179 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 180 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 181 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LBU then
|
| 182 |
+
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 183 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_BYTE;
|
| 184 |
+
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 185 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 186 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 187 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 188 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 189 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
@@ -25,6 +25,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 25 |
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LW,
|
|
|
|
| 28 |
OP_LED
|
| 29 |
);
|
| 30 |
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LW,
|
| 28 |
+
OP_LBU,
|
| 29 |
OP_LED
|
| 30 |
);
|
| 31 |
|
LHU is similar.
|
@@ -61,7 +61,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 61 |
|
| 62 |
v_mem_result(31 downto 8) := (others => '0');
|
| 63 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 64 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 65 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
| 66 |
v_mem_result := mem_res;
|
| 67 |
else
|
|
@@ -172,7 +178,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 172 |
-- LBU
|
| 173 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LBU;
|
| 174 |
elsif funct3 = "101" then
|
| 175 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 176 |
else
|
| 177 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 178 |
end if;
|
|
|
|
| 61 |
|
| 62 |
v_mem_result(31 downto 8) := (others => '0');
|
| 63 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 64 |
+
if write_input.mem_addr = "00" then
|
| 65 |
+
v_mem_result(15 downto 0) := mem_res(15 downto 0);
|
| 66 |
+
else
|
| 67 |
+
v_mem_result(15 downto 0) := mem_res(31 downto 16);
|
| 68 |
+
end if;
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
v_mem_result(31 downto 16) := (others => '0');
|
| 71 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
| 72 |
v_mem_result := mem_res;
|
| 73 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 178 |
-- LBU
|
| 179 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LBU;
|
| 180 |
elsif funct3 = "101" then
|
| 181 |
+
-- LHU
|
| 182 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LHU;
|
| 183 |
else
|
| 184 |
v_decode_output.is_invalid := '1';
|
| 185 |
end if;
|
|
@@ -184,6 +184,12 @@ begin
|
|
| 184 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 185 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 186 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 187 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 188 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 189 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
|
|
| 184 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 185 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 186 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 187 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 188 |
+
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 189 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
| 190 |
+
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 191 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 192 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 193 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 194 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 195 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
@@ -26,6 +26,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LW,
|
| 28 |
OP_LBU,
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
OP_LED
|
| 30 |
);
|
| 31 |
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LW,
|
| 28 |
OP_LBU,
|
| 29 |
+
OP_LHU,
|
| 30 |
OP_LED
|
| 31 |
);
|
| 32 |
|
LB is similar to LBU but we need to add sign extension.
|
@@ -59,7 +59,11 @@ begin
|
|
| 59 |
v_mem_result(7 downto 0) := mem_res(31 downto 24);
|
| 60 |
end if;
|
| 61 |
|
| 62 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 63 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 64 |
if write_input.mem_addr = "00" then
|
| 65 |
v_mem_result(15 downto 0) := mem_res(15 downto 0);
|
|
@@ -168,7 +172,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 168 |
v_decode_output.destination_reg := rd;
|
| 169 |
|
| 170 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 171 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 172 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 173 |
-- TODO: LH
|
| 174 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
|
|
|
| 59 |
v_mem_result(7 downto 0) := mem_res(31 downto 24);
|
| 60 |
end if;
|
| 61 |
|
| 62 |
+
if write_input.mem_sign_extend = '1' then
|
| 63 |
+
v_mem_result(31 downto 8) := (others => v_mem_result(7));
|
| 64 |
+
else
|
| 65 |
+
v_mem_result(31 downto 8) := (others => '0');
|
| 66 |
+
end if;
|
| 67 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_HALFWORD then
|
| 68 |
if write_input.mem_addr = "00" then
|
| 69 |
v_mem_result(15 downto 0) := mem_res(15 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 172 |
v_decode_output.destination_reg := rd;
|
| 173 |
|
| 174 |
if funct3 = "000" then
|
| 175 |
+
-- LB
|
| 176 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LB;
|
| 177 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 178 |
-- TODO: LH
|
| 179 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
|
@@ -184,6 +184,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 184 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 185 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 186 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 187 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 188 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 189 |
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
|
|
|
| 184 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 185 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 186 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 187 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LB then
|
| 188 |
+
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 189 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_BYTE;
|
| 190 |
+
v_output.mem_sign_extend := '1';
|
| 191 |
+
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 192 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 193 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 194 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 195 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 196 |
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
|
@@ -24,6 +24,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 24 |
OP_SB,
|
| 25 |
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
OP_LW,
|
| 28 |
OP_LBU,
|
| 29 |
OP_LHU,
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
OP_SB,
|
| 25 |
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
+
OP_LB,
|
| 28 |
OP_LW,
|
| 29 |
OP_LBU,
|
| 30 |
OP_LHU,
|
Finally, we get to LH which is similar to LB again.
|
@@ -71,7 +71,11 @@ begin
|
|
| 71 |
v_mem_result(15 downto 0) := mem_res(31 downto 16);
|
| 72 |
end if;
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 75 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
| 76 |
v_mem_result := mem_res;
|
| 77 |
else
|
|
@@ -175,7 +179,8 @@ begin
|
|
| 175 |
-- LB
|
| 176 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LB;
|
| 177 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 178 |
-
--
|
|
|
|
| 179 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 180 |
-- LW
|
| 181 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LW;
|
|
|
|
| 71 |
v_mem_result(15 downto 0) := mem_res(31 downto 16);
|
| 72 |
end if;
|
| 73 |
|
| 74 |
+
if write_input.mem_sign_extend = '1' then
|
| 75 |
+
v_mem_result(31 downto 16) := (others => v_mem_result(15));
|
| 76 |
+
else
|
| 77 |
+
v_mem_result(31 downto 16) := (others => '0');
|
| 78 |
+
end if;
|
| 79 |
elsif write_input.mem_size = SIZE_WORD then
|
| 80 |
v_mem_result := mem_res;
|
| 81 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 179 |
-- LB
|
| 180 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LB;
|
| 181 |
elsif funct3 = "001" then
|
| 182 |
+
-- LH
|
| 183 |
+
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LH;
|
| 184 |
elsif funct3 = "010" then
|
| 185 |
-- LW
|
| 186 |
v_decode_output.operation := OP_LW;
|
|
@@ -197,6 +197,13 @@ begin
|
|
| 197 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 198 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 199 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 200 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 201 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 202 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
|
|
| 197 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 198 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 199 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 200 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LH then
|
| 201 |
+
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 202 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
| 203 |
+
v_output.mem_sign_extend := '1';
|
| 204 |
+
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 205 |
+
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 206 |
+
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 207 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 208 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 209 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
|
@@ -25,6 +25,7 @@ package core_types is
|
|
| 25 |
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LB,
|
|
|
|
| 28 |
OP_LW,
|
| 29 |
OP_LBU,
|
| 30 |
OP_LHU,
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
OP_SH,
|
| 26 |
OP_SW,
|
| 27 |
OP_LB,
|
| 28 |
+
OP_LH,
|
| 29 |
OP_LW,
|
| 30 |
OP_LBU,
|
| 31 |
OP_LHU,
|
The execute stage now contains a lot of duplicated code, so we'll do a bit of cleanup.
|
@@ -172,40 +172,25 @@ begin
|
|
| 172 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
| 173 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 174 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 175 |
-
elsif input.operation = OP_LW
|
|
|
|
| 176 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 177 |
-
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_WORD;
|
| 178 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
|
|
|
| 179 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 180 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 181 |
-
|
| 182 |
-
|
| 183 |
-
|
| 184 |
-
|
| 185 |
-
|
| 186 |
-
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
|
| 189 |
-
|
| 190 |
-
|
| 191 |
-
|
| 192 |
-
|
| 193 |
-
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 194 |
-
elsif input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 195 |
-
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 196 |
-
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
| 197 |
-
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 198 |
-
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 199 |
-
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 200 |
-
elsif input.operation = OP_LH then
|
| 201 |
-
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 202 |
-
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
| 203 |
-
v_output.mem_sign_extend := '1';
|
| 204 |
-
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 205 |
-
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 206 |
-
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 207 |
-
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 208 |
-
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 209 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 210 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 211 |
else
|
|
|
|
| 172 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
| 173 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 174 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 175 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LB or input.operation = OP_LH or input.operation = OP_LW or
|
| 176 |
+
input.operation = OP_LBU or input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 177 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
|
|
|
| 178 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 179 |
+
|
| 180 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 181 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 182 |
+
|
| 183 |
+
if input.operation = OP_LB or input.operation = OP_LH then
|
| 184 |
+
v_output.mem_sign_extend := '1';
|
| 185 |
+
end if;
|
| 186 |
+
|
| 187 |
+
if input.operation = OP_LB or input.operation = OP_LBU then
|
| 188 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_BYTE;
|
| 189 |
+
elsif input.operation = OP_LH or input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 190 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_HALFWORD;
|
| 191 |
+
else
|
| 192 |
+
v_output.mem_size := SIZE_WORD;
|
| 193 |
+
end if;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 194 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LED then
|
| 195 |
led <= input.operand1(7 downto 0);
|
| 196 |
else
|
Come to think of it, reads and writes should cause an exception when they are misaligned, but we did not implement exceptions yet. Better add some comments to remind ourselves when we get to that.
|
@@ -157,6 +157,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 157 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1000";
|
| 158 |
end if;
|
| 159 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SH then
|
|
|
|
| 160 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 161 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 162 |
|
|
@@ -168,12 +169,14 @@ begin
|
|
| 168 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1100";
|
| 169 |
end if;
|
| 170 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
|
|
|
| 171 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 172 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
| 173 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 174 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 175 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LB or input.operation = OP_LH or input.operation = OP_LW or
|
| 176 |
input.operation = OP_LBU or input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
|
|
|
| 177 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 178 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 179 |
|
|
|
|
| 157 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1000";
|
| 158 |
end if;
|
| 159 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SH then
|
| 160 |
+
-- TODO: a misaligned store should generate an exception
|
| 161 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 162 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 163 |
|
|
|
|
| 169 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1100";
|
| 170 |
end if;
|
| 171 |
elsif input.operation = OP_SW then
|
| 172 |
+
-- TODO: a misaligned store should generate an exception
|
| 173 |
v_mem_req.active := '1';
|
| 174 |
v_mem_req.write_enable := "1111";
|
| 175 |
v_mem_req.address := input.operand1;
|
| 176 |
v_mem_req.value := input.operand2;
|
| 177 |
elsif input.operation = OP_LB or input.operation = OP_LH or input.operation = OP_LW or
|
| 178 |
input.operation = OP_LBU or input.operation = OP_LHU then
|
| 179 |
+
-- TODO: a misaligned load should generate an exception
|
| 180 |
v_output.use_mem := '1';
|
| 181 |
v_output.mem_addr := input.operand1(1 downto 0);
|
| 182 |
|
Now, to test the loads and stores we add a small test program to our instruction memory, which is the result of assembling
li x1, 0xdeadbeef
# stores
sw x1, 0(x0)
sh x1, 4(x0)
sh x1, 10(x0)
sb x1, 12(x0)
sb x1, 17(x0)
sb x1, 22(x0)
sb x1, 27(x0)
# unsigned loads
lw x2, 0(x0)
lhu x3, 4(x0)
lhu x4, 10(x0)
lbu x5, 12(x0)
lbu x6, 17(x0)
lbu x7, 22(x0)
lbu x8, 27(x0)
# signed loads
lh x9, 4(x0)
lh x10, 10(x0)
lb x11, 12(x0)
lb x12, 17(x0)
lb x13, 22(x0)
lb x14, 27(x0)
hang:
j hang
|
@@ -18,10 +18,12 @@ end fetch;
|
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
architecture rtl of fetch is
|
| 21 |
-
type instruction_memory_t is array(0 to
|
| 22 |
signal imem: instruction_memory_t := (
|
| 23 |
-
X"
|
| 24 |
-
X"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
);
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
signal pc: unsigned(31 downto 0) := (others => '0');
|
|
@@ -35,7 +37,7 @@ begin
|
|
| 35 |
pc <= pc + 4;
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
output.is_active <= '1';
|
| 38 |
-
output.instr <= imem(to_integer(pc(
|
| 39 |
output.pc <= std_logic_vector(pc);
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
assert jump = '0' report "Fetching and jumping at the same cycle is not supported";
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
architecture rtl of fetch is
|
| 21 |
+
type instruction_memory_t is array(0 to 31) of std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
|
| 22 |
signal imem: instruction_memory_t := (
|
| 23 |
+
X"deadc0b7", X"eef08093", X"00102023", X"00101223", X"00101523", X"00100623", X"001008a3", X"00100b23",
|
| 24 |
+
X"00100da3", X"00002103", X"00405183", X"00a05203", X"00c04283", X"01104303", X"01604383", X"01b04403",
|
| 25 |
+
X"00401483", X"00a01503", X"00c00583", X"01100603", X"01600683", X"01b00703", X"0000006f", X"00000000",
|
| 26 |
+
X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000", X"00000000"
|
| 27 |
);
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
signal pc: unsigned(31 downto 0) := (others => '0');
|
|
|
|
| 37 |
pc <= pc + 4;
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
output.is_active <= '1';
|
| 40 |
+
output.instr <= imem(to_integer(pc(6 downto 2)));
|
| 41 |
output.pc <= std_logic_vector(pc);
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
assert jump = '0' report "Fetching and jumping at the same cycle is not supported";
|
Simulating this for 1500 ns, we get the following waveforms.
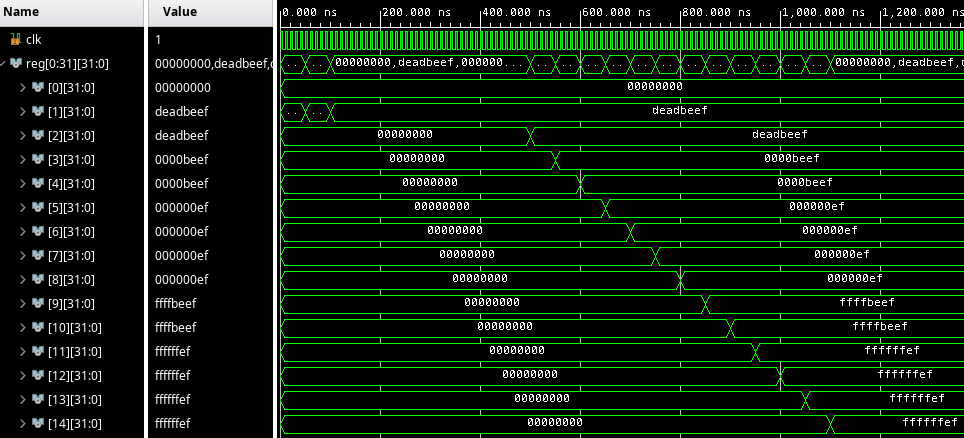
For the unsigned loads we expect
- The
LWinstruction to load the full word0xdeadbeef - The
LHUinstructions to load0x0000beef - The
LBUinstructions to load0x000000ef
For the signed loads we expect
- The
LHUinstructions to load0xffffbeef - The
LBUinstructions to load0xffffffef
This all looks good, so we're done with the load and store instructions for now!